Introduction to the Eastern Indigo Snake
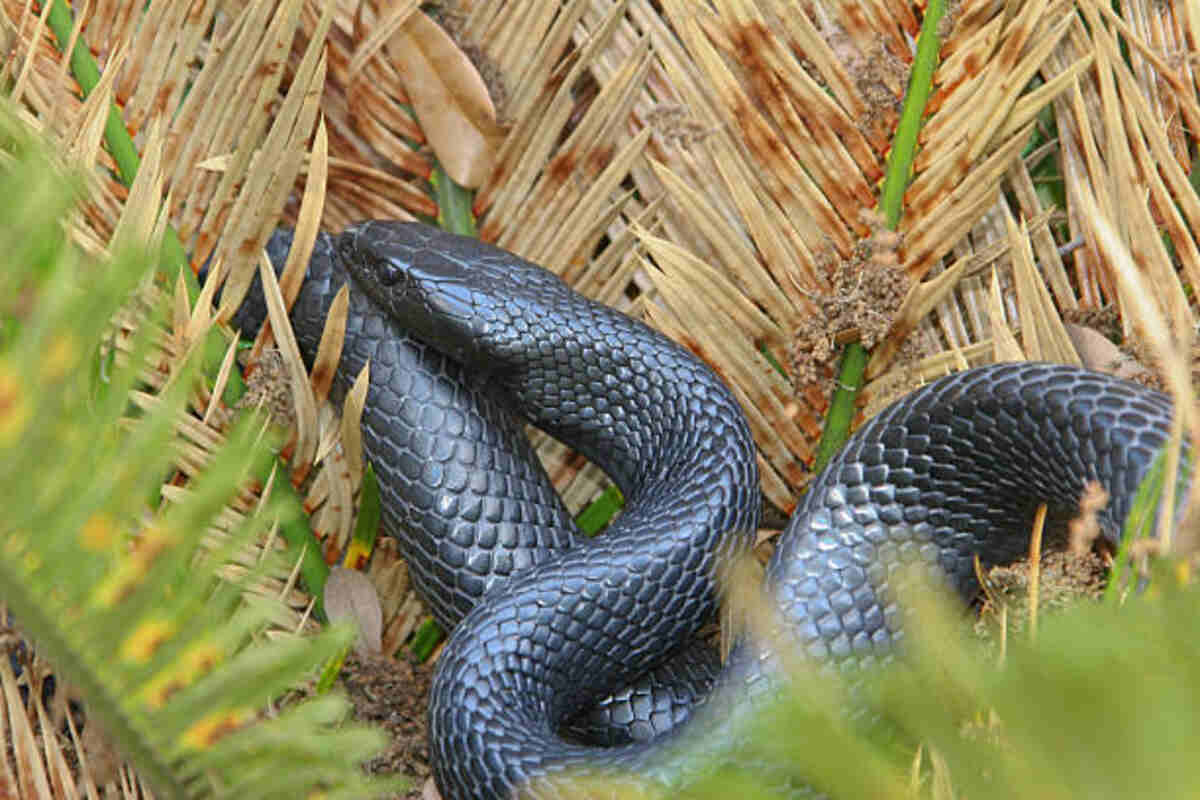
The Eastern Indigo Snake is one of North America’s most fascinating and enigmatic reptile species. Native to the southeastern United States, this snake is celebrated not only for its striking appearance—a shimmering blend of blue-black scales—but also for its vital role in maintaining the ecological balance in its habitat. In this article, we’ll dive into the many challenges it faces today, discuss ongoing conservation efforts, and explore future strategies that might ensure its survival. Obtain the Best information about eastern indigo snakes for sale.
You might wonder why this snake garners so much attention. Well, for starters, it’s one of the longest native snakes in the United States and a top predator in its ecosystem. Its diet includes a wide range of prey, from small mammals to amphibians and even other reptiles, which makes it crucial for controlling pest populations. Additionally, its presence indicates a healthy, well-balanced ecosystem, acting as a bioindicator for environmental changes.
Despite its importance, the Eastern Indigo Snake is increasingly coming under threat. Whether it’s due to urban expansion or unforeseen consequences of climate change, multiple factors are undermining its survival. In recent years, habitat loss, road mortality, and invasive species have all played a part in reducing its population. Contractions like “it’s” and “don’t” make this read accessible while not undermining the formal tone necessary for discussing such a serious subject.
Moreover, early conservation initiatives have provided hope, and ongoing research is crucial in keeping track of these threats. For example, community-based conservation projects and federal initiatives have been pivotal in creating sanctuaries that protect the snake’s natural habitat. The Eastern Indigo Snake is more than just an animal; it represents the challenges faced by many species caught between human development and the relentless pressures of a changing environment.
In the coming sections, we’ll explore the unique habitat of the Eastern Indigo Snake and the various challenges it encounters. We’ll also look at how environmental shifts—especially those tied to climate change—impact its survival. By understanding the intricate details of its life and the risks it faces, we can better appreciate why preserving this species is crucial for our shared natural heritage.
Understanding the Habitat
The Eastern Indigo Snake calls a variety of ecosystems home, from longleaf pine forests to coastal dunes. Its habitat spans a significant geographic area in the southeastern United States, where it plays an indispensable role in controlling populations of small mammals and other reptiles. Understanding its habitat is key to addressing the threats it faces.
Geographic Distribution
These snakes are primarily found in states like Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and South Carolina. Their distribution is closely tied to the availability of natural, undisturbed lands. Urban sprawl and agricultural developments are slowly encroaching upon these areas, leading to fragmentation of what was once a contiguous and thriving ecosystem.
Ecosystem Role
In their natural habitats, Eastern Indigo Snakes help regulate the balance between predators and prey. They are not picky eaters, and their varied diet allows them to thrive in multiple environmental conditions. This adaptability has long been one of their greatest strengths, yet it also makes them particularly vulnerable when sudden changes occur. When urban development replaces natural landscapes, the ecological network is disrupted, and species like the Eastern Indigo Snake lose critical access to food and shelter.
The snake’s presence signals a robust ecosystem. Its role as an apex predator means that any decline in its numbers might indicate broader ecological imbalances. Hence, protecting its habitat benefits not only the snake but a wide array of other species sharing the same environment.
Moreover, preserving natural habitats is fundamental to mitigating some of the adverse effects of climate change. Intact ecosystems can act as buffers against environmental extremes, providing resilience in the face of shifting weather patterns and habitat destruction. As we transition into discussing the various threats, it becomes evident that human-induced habitat changes are a primary concern for this species.
Major Threats Facing the Eastern Indigo Snake Today
The Eastern Indigo Snake faces a multitude of challenges in the wild. In this section, we’ll examine in detail the primary threats that jeopardize its survival, spanning from habitat loss to human-wildlife conflicts. Each threat interconnects with the others, creating a complex web of challenges that require immediate and sustained conservation efforts.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
One of the most pressing issues is the loss of natural habitat. Rapid urbanization, commercial development, and expanding agricultural activities have led to significant habitat fragmentation. When large, contiguous tracts of forest are divided into smaller patches, the connectivity necessary for species migration and genetic diversity is compromised. The Eastern Indigo Snake, which roams across large territories, finds its movement severely restricted by roads, fences, and urban sprawl. This not only limits their access to vital resources such as prey and shelter but also increases their vulnerability to predators and environmental stressors.
Habitat fragmentation also contributes to the decline in population density. As suitable habitats shrink, snakes are forced into smaller areas, where competition for food intensifies, and the risk of inbreeding rises. These factors can lead to a weakened gene pool and reduced resilience against diseases and environmental changes. The domino effect of these changes cannot be overstated; each fragmented habitat represents a lost opportunity for the species to thrive naturally.
Road Mortality
Another significant threat is road mortality. As human developments spread, roads crisscross the once uninterrupted landscapes. Eastern Indigo Snakes, in their natural quest for food and mating opportunities, often cross these roads. Unfortunately, many are struck by vehicles, resulting in high mortality rates. This problem is exacerbated in regions where traffic density is high and roads are not designed with wildlife corridors in mind. The loss of even a few individuals can have cascading effects on local populations, especially given the snake’s already fragment,, ed habitat.
Road mortality is not just a statistic—it’s a vivid illustration of how human progress can inadvertently endanger native species. In some areas, conservationists are experimenting with wildlife crossings and road underpasses. These measures, though costly and logistically challenging, have proven effective in reducing collisions and maintaining connectivity between fragmented habitats.
Invasive Species
Invasive species also pose a major challenge. Non-native predators and competitors can alter the delicate balance of ecosystems. When invasive species establish themselves, they often outcompete local fauna for resources. In some cases, these invaders may introduce diseases to which the Eastern Indigo Snake has little to no resistance. The introduction of invasive plants can change the structure of the habitat itself, making it less suitable for the snake’s needs. This insidious threat often goes unnoticed until its impacts become widespread and difficult to reverse.
Climate Change Impact
Climate change is an overarching threat that amplifies all the other challenges. Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns directly affect the Eastern Indigo Snake’s habitat. For instance, prolonged droughts or intense rainfall events can drastically alter the ecosystem dynamics. Changes in climate can also shift the distribution of prey species, further destabilizing the food chain. Moreover, extreme weather events such as hurricanes or floods can decimate locals” climate changes critical habitat areas in a matter of hours.
Human-Wildlife Conflict
Direct conflict with humans further complicates the survival of the Eastern Indigo Snake. In many areas, these snakes are misunderstood and often feared. Local residents sometimes kill them on sight, mistakenly believing they are dangerous. This human-wildlife conflict, fueled by myths and misconceptions, contributes to unnecessary fatalitiesResdetsResidentsnitiatives have tried to bridge the gap between myth and reality, but deep-seated fears persist in some communities.
In summary, the convergence of habitat loss, road mortality, invasive species, climate change, and direct human conflict creates a perfect storm for the Eastern Indigo Snake. It’s a classic case where multiple environmental stressors interact, leaving the species with few safe havens. Each of these threats is daunting on its own, but together they underscore the urgent need for comprehensive conservation measures.
Conservation efforts that address one threat in isolation are unlikely to succeed. Instead, an integrated approach t, that considers the cumulative impact of all these factors is required. Researchers and policymakers must work together, ensuring that strategies are both holistic and adaptable. Initiatives such as creating wildlife corridors, investing in community education, and enforcing habitat protection laws are vital to ensure that interdisciplinary research that combines ecology, climatology, and urban planning could provide new insights into mitigating these threats.
Ultimately, while the challenges are severe, the ongoing efforts of dedicated conservationists offer a glimmer of hope. By understanding and addressing each of these threats, we can work towards a future where the Eastern Indigo Snake thrives in a safe and healthy environment.
Impact of Climate Change on Eastern Indigo Snake Survival
Climate change is a pervasive threat that magnifies many of the challenges faced by wildlife today, and the Eastern Indigo Snake is no exception. Changing weather patterns, more frequent extreme weather events, and shifting seasonal cycles directly influence the habitats and behaviors of these snakes.
Changing Weather Patterns
As global temperatures continue to rise, the Eastern Indigo Snake experiences alterations in its breeding cycles and prey availability. Unpredictable weather can disrupt the delicate balance of its ecosystem. For example, unseasonably cold spells or extended periods of heat may force the snake to seek refuge, reducing its hunting opportunities and thereby affecting its energy balance. This disruption is compounded when prey species also shift their distribution or behavior in response to the same climatic changes.
Furthermore, erratic weather patterns can affect the very structure of the habitat. Prolonged droughts may lead to the degradation of wetland areas and forested regions, while intense rainfall and flooding can erode soil and destroy vegetation. These environmental changes directly impact the snake’s ability to find shelter and reproduce successfully.
Adaptation Challenges
While the Eastern Indigo Snake is known for its adaptability, rapid environmental changes pose a significant challenge. The snake’s physiological and behavioral adaptations have evolved over millennia to suit stable conditions. However, when climate change accelerates environmental shifts, the snake may not be able to adjust quickly enough. This lag in adaptation can lead to a decline in population numbers as individuals struggle to cope with the new normal.
Scientists are actively studying these impacts, employing modern technologies like satellite imagery and temperature sensors to monitor changes in the snake’s habitat. The integration of these tools in conservation strategies has been promising, yet the overall uncertainty of future climate scenarios continues to be a major concern.
In short, the multifaceted impacts of climate change—altering weather patterns, degrading habitats, and challenging the species’ adaptability—further complicate the survival prospects of the Eastern Indigo Snake. While researchers are continually gathering data to better understand these dynamics, it’s clear that mitigating climate change is a crucial component of any long-term conservation strategy.
Human-Induced Environmental Stressors
Beyond climate change, human activities remain a primary driver of environmental stress. Rapid urbanization, agricultural expansion, and other developmental projects have directly altered the landscapes where the Eastern Indigo Snake once thrived. These activities not only reduce available habitat but also introduce pollutants and disturbances that can have cascading effects on local ecosystems.
Urbanization Effects
The steady march of urban sprawl has led to significant changes in the natural environment. As cities expand, natural habitats are often fragmented, turning once-contiguous forests into isolated patches. For the Eastern Indigo Snake, these fragmented habitats can mean increased exposure to road traffic and reduced access to critical resources. Moreover, urban areas tend to bring with them a host of pollutants—from chemical runoff to noise pollution—which further degrade the quality of the environment.
Agricultural Expansion
Similarly, the expansion of agriculture has transformed vast areas of natural land into farmland. While farming is essential for fodegradesng growing populations, its side effects, such as pesticide use and soil degradation, have far-reaching impacts on local wildlife. The intensive use of chemicals not only affects the prey populations but also the overall health of the ecosystems the snake relies upon.
It’s important to note that these stressors are not isolated. The interaction affects not only the population but human-induced factcoatingses a compounded effect. Each element contributes to an environment that is less hospitable to native species, including the Eastern Indigo Snake.
Conservation Efforts and Strategies
The good news is that despite these daunting challenges, there are robust conservation efforts underway to protect the Eastern Indigo Snake. A multi-pronged approach is essential to address the myriad threats this species faces—from habitat destruction to climate change and human-wildlife conflict.
Federal and State Initiatives
Government agencies at both the federal and state levels have recognized the urgent need to protect the Eastern Indigo Snake. Various initiatives are aimed at preserving large tracts of natural habitat and establishing wildlife corridors to reconnect fragmented populations. Programs led by the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service, for instance, have implemented habitat restoration projects that benefit not only this snake but countless other species. Legislative measures, including stricter land-use regulations, have been instrumental in curbing further habitat destruction.
NGO Contributions
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play an equally vital role in conservation. These groups often spearhead grassroots campaigns that raise awareness about the importance of the Eastern Indigo Snake. They also work on the ground to implement conservation projects, such as creating safe passages over roads and organizing community-based habitat monitoring. Collaboration between NGOs, government bodies, and local communities has proven to be one of the most effective ways to combat the multifaceted threats facing this species.
Community Engagement
Local communities are increasingly being recognized as essential partners in conservation. Educational programs aimed at dispelling myths about the Eastern Indigo Snake have helped reduce instances of human-wildlife conflict. In many areas, residents now understand that the snake is not a menace but a critical part of the local ecosystem. Workshops, school programs, and volunteer initiatives have all contributed to a growing sense of stewardship toward local wildlife.
Innovative Conservation Strategies
Modern technology is also making a difference. Researchers are using GPS tracking, remote sensing, and data analytics to monitor snake populations more accurately. These innovative approaches provide critical data that help shape future conservation plans. For example, real-time monitoring can alert conservationists to dangerous trends, such as increased road mortality or rapid habitat degradation, allowing them to act swiftly.
Conservation strategies are increasingly holistic. Instead of focusing on a single threat, integrated management plans address multiple factors simultaneously. This might include habitat restoration projects that not only rebuild lost environments but also incorporate climate resilience measures. Furthermore, collaborative research initiatives—linking academic institutions with conservation organizations—ensure that the latest scientific insights are applied to real-world challenges.
For more detailed information on governmental conservation efforts, check out the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service.
In conclusion, while the threats to the Eastern Indigo Snake are significant, the comprehensive conservation efforts underway provide a hopeful outlook. By combining government policies, NGO work, community engagement, and innovative research, there’s a concerted push toward ensuring that this remarkable species not only survives but thrives for generations to come.
Research, Monitoring, and Future Outlook
The future of the Eastern Indigo Snake depends heavily on our ability to understand its needs through robust research and continuous monitoring. Scientists and conservationists are joining forces to study this species in depth, using a variety of tools to track its population trends, behavioral patterns, and responses to environmental changes.
Current Studies and Data Collection
Recent research efforts have focused on long-term population monitoring. Field studies, which involve tracking individual snakes using radio telemetry and GPS devices, have provided invaluable data on migration patterns and habitat use. These studies reveal that the Eastern Indigo Snake is far more mobile than once believed, covering vast areas in search of food and mates. Such data are critical when planning conservation strategies that ensure connectivity between fragmented habitats.
Technology in Conservation
Advancements in technology have transformed how conservationists monitor wildlife. Remote sensing, drone surveillance, and real-time data analytics now allow for more precise tracking of habitat changes. These technologies not only help in mapping the snake’s distribution but also in identifying areas that are most at risk of degradation. With these tools, researchers can quickly respond to emerging threats and adjust conservation measures accordingly.
Moreover, citizen science initiatives have gained momentum. By involving local communities in data collection—often through mobile apps and online platforms—researchers can gather large volumes of information across broad geographic areas. This collaborative approach not only enriches the data pool but also fosters a sense of responsibility and awareness among community members.
Recovery Plans and Future Predictions
Looking forward, recovery plans for the Eastern Indigo Snake emphasize adaptive management. This approach allows conservation strategies to evolve based on new research findings and changing environmental conditions. Experts predict that without intervention, current trends could lead to further declines in snake populations. However, with concerted efforts, there is significant potential for recovery. Future strategies include establishing additional protected areas, enhancing wildlife corridors, and implementing targeted educational campaigns to mitigate human-wildlife conflicts.
Collaborative research between universities, governmental agencies, and NGOs is paving the way for more effective conservation policies. By sharing data and resources, these groups can develop comprehensive plans that address the root causes of habitat degradation and population decline. The integration of ecological studies with advanced technological tools offers a promising path forward, ensuring that the Eastern Indigo Snake receives the attention and protection it deserves.
In summary, while the challenges remain daunting, the future outlook for the Eastern Indigo Snake is cautiously optimistic. With ongoing research, innovative monitoring techniques, and adaptive recovery plans, there’s every reason to believe that this iconic species can overcome the current threats and continue to play its vital role in the ecosystem.
FAQs
Q1: What makes the Eastern Indigo Snake so important to its ecosystem?
A1: The Eastern Indigo Snake is a top predator in its habitat, helping to control populations of small mammals, amphibians, and other reptiles. Its presence indicates a healthy ecosystem, as it relies on a balanced food web and undisturbed habitat to thrive.
Q2: How does habitat fragmentation affect the Eastern Indigo Snake?
A2: Habitat fragmentation reduces the available territory for the snake, limits its access to food and shelter, and increases the risk of road mortality and inbreeding. Smaller, isolated populations are more vulnerable to extinction due to reduced genetic diversity and increased environmental stress.
Q3: What are the primary human activities that threaten the Eastern Indigo Snake?
A3: Key threats include urbanization, agricultural expansion, road construction, and associated habitat destruction. These activities not only fragment natural habitats but also introduce pollutants and create physical barriers that limit the snake’s movement.
Q4: In what ways is climate change impacting the Eastern Indigo Snake?
A4: Climate change alters weather patterns, leading to extreme events like droughts and floods, which degrade the snake’s habitat. Shifts in temperature and precipitation can disrupt breeding cycles and affect the availability of prey, further stressing the species.
Q5: What conservation efforts are in place to protect the Eastern Indigo Snake?
A5: A combination of federal and state initiatives, NGO programs, and community engagement efforts work together to protect this species. Strategies include habitat restoration, the creation of wildlife corridors, public education campaigns, and the implementation of adaptive management plans.
Q6: How can local communities contribute to the conservation of the Eastern Indigo Snake?
A6: Communities can help by participating in educational programs, reporting sightings, supporting habitat preservation initiatives, and advocating for policies that protect local ecosystems. Increased public awareness reduces human-wildlife conflicts and promotes a more harmonious coexistence.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, the Eastern Indigo Snake faces a complex array of threats that demand a multifaceted response. From habitat loss and road mortality to the expansive impacts of climate change and human-induced environmental stressors, every challenge underscores the need for comprehensive, well-coordinated conservation strategies.
Throughout this article, we’ve seen that while the challenges are significant, there is also a determined effort from government bodies, NGOs, researchers, and local communities to turn the tide in favor of this remarkable species. The collaborative spirit that drives these conservation initiatives is a beacon of hope—a sign that even in the face of daunting environmental changes, proactive and adaptive management can make a real difference.
The path ahead isn’t easy, and continuous research and community engagement will be essential. Yet, with ongoing advancements in technology and a deepening understanding of the intricate relationships within ecosystems, there’s every reason to remain optimistic about the future of the Eastern Indigo Snake.
By remaining committed to preserving natural habitats, promoting sustainable development, and ensuring that conservation policies are both adaptive and science-driven, we can help secure a future where the Eastern Indigo Snake not only survives but thrives as an integral part of our shared natural heritage.
Read also:


 Home
Home